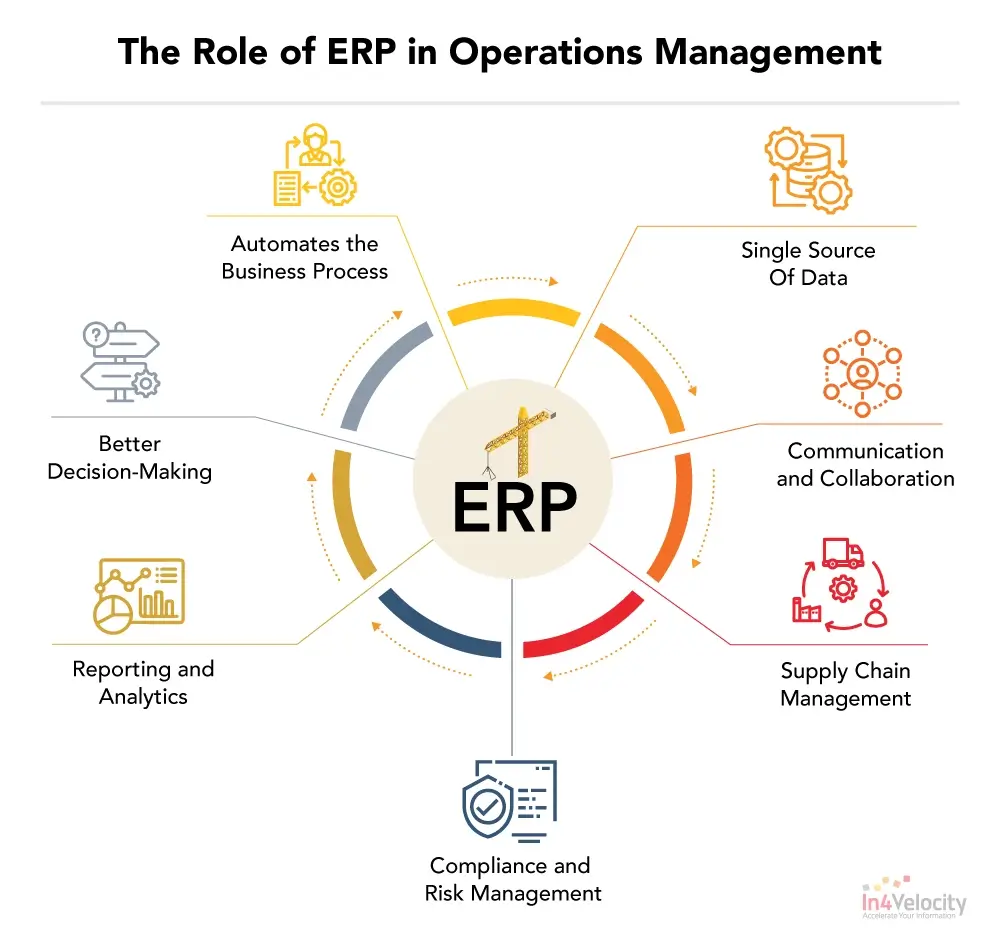
In today’s complex business environment, compliance with various regulatory requirements is crucial for the sustainability and success of any organization. Regulatory compliance encompasses a range of activities, including adhering to industry standards, government regulations, and internal policies. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software plays a vital role in managing and ensuring compliance. Here’s how ERP systems contribute to regulatory management:
1. Centralized Data Management
ERP systems centralize data across different business functions—such as finance, HR, supply chain, and manufacturing—into a single, unified platform. This centralized data repository ensures that all information is accurate, consistent, and up-to-date. For compliance purposes, having a single source of truth reduces the risk of errors and discrepancies that could lead to regulatory breaches.
2. Automated Compliance Reporting
One of the most significant benefits of ERP software is its ability to automate compliance reporting. ERP systems can generate reports required by regulatory bodies, such as tax reports, financial statements, and audit trails. Automation not only streamlines the reporting process but also reduces the likelihood of human error, ensuring that reports are accurate and submitted on time.
3. Real-Time Monitoring and Alerts
ERP systems offer real-time monitoring of various business processes and transactions. This capability allows organizations to track compliance-related activities and identify potential issues before they escalate. For example, ERP systems can provide alerts for anomalies or deviations from standard procedures, enabling timely corrective actions.
4. Enhanced Audit Trails
Regulatory compliance often requires maintaining detailed records of business activities. ERP systems create comprehensive audit trails by documenting every transaction and change made within the system. These audit trails are crucial during internal and external audits, providing transparency and evidence that regulatory requirements are being met.
5. Integration with Compliance Tools
Modern ERP systems can integrate with specialized compliance tools and modules designed for industry-specific regulations. For instance, ERP systems can work in conjunction with tools that handle environmental regulations, data privacy laws (such as GDPR), and industry-specific standards (such as ISO certifications). This integration ensures that compliance requirements are continuously monitored and addressed.
6. Role-Based Access Control
To safeguard sensitive data and ensure compliance with data protection regulations, ERP systems offer role-based access control. This feature restricts access to information based on user roles and responsibilities, ensuring that only authorized personnel can view or modify critical data. This helps prevent unauthorized access and potential breaches of regulatory requirements.
7. Documentation and Record Keeping
Regulations often mandate the retention of specific records and documentation for a set period. ERP systems facilitate proper documentation and record-keeping by storing digital records securely. This ensures that organizations can easily access historical data when required for audits or compliance checks.
8. Regulatory Updates and Adaptation
Compliance requirements are subject to change as new regulations are introduced or existing ones are amended. ERP vendors often provide updates to their software to address these changes. Staying current with ERP updates helps organizations adapt to new regulations without major disruptions to their operations.
9. Improved Data Accuracy and Integrity
Accurate and reliable data is fundamental for compliance. ERP systems enhance data accuracy through standardized processes and validation checks. By minimizing data errors and inconsistencies, ERP systems help organizations maintain compliance with regulatory standards that depend on precise data.
10. Training and Support
ERP vendors typically offer training and support to help organizations understand and utilize compliance features effectively. This training ensures that employees are knowledgeable about how to use the ERP system for regulatory purposes and are aware of any changes or updates related to compliance.
Conclusion
ERP software plays a crucial role in managing compliance and regulatory requirements by centralizing data, automating reporting, and providing real-time monitoring. By leveraging ERP systems, organizations can streamline their compliance processes, reduce risks, and ensure they meet regulatory standards efficiently. As regulatory environments continue to evolve, ERP systems will remain an essential tool for navigating the complexities of compliance management.