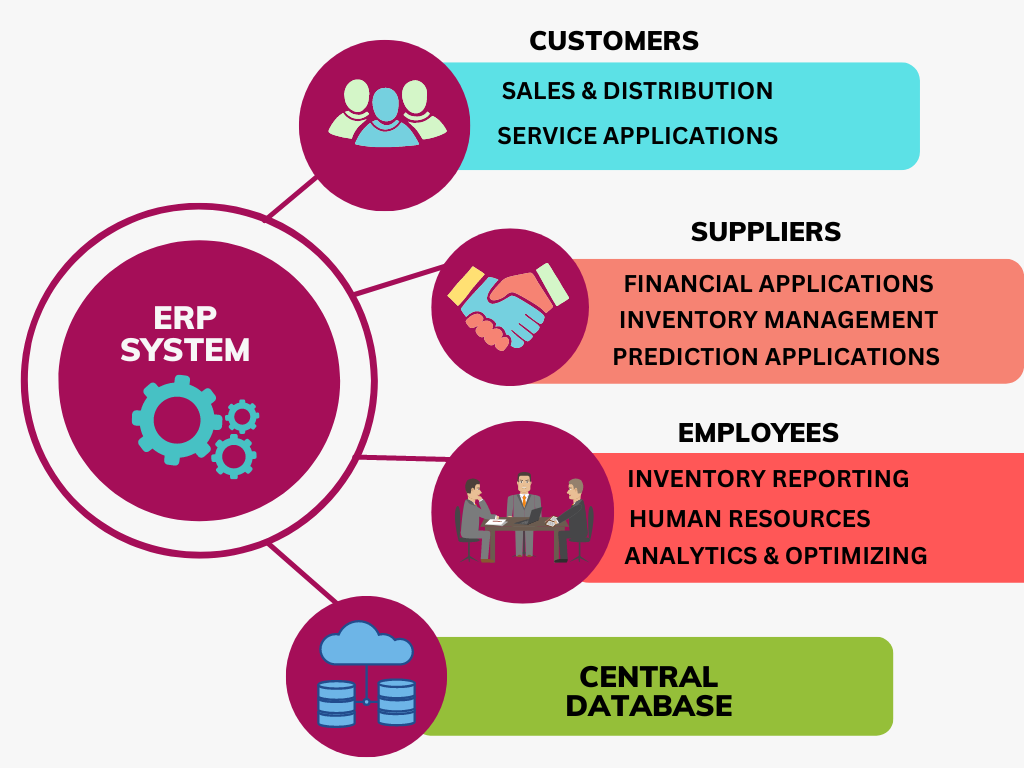
In today’s fast-paced retail environment, managing inventory efficiently and maximizing sales are crucial for maintaining competitiveness and profitability. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software offers a comprehensive solution that integrates various business processes into a unified system. In this article, we’ll explore how ERP for retail can significantly enhance inventory management and drive sales growth.
1. Streamlined Inventory Management
One of the core benefits of ERP software for retail is its ability to streamline inventory management. Here’s how it achieves this:
Real-Time Inventory Tracking: ERP systems provide real-time visibility into inventory levels across all sales channels. This means retailers can monitor stock levels, track shipments, and manage stock reordering more effectively. With up-to-date information, businesses can avoid overstocking or stockouts, which directly impacts sales and customer satisfaction.
Automated Reordering: ERP software can automate the reordering process based on predefined thresholds. When inventory levels drop below a certain point, the system can trigger automatic purchase orders or alerts to reorder stock. This reduces manual intervention, minimizes the risk of human error, and ensures that popular products are always available.
Centralized Data Management: With ERP, all inventory data is centralized in one system. This eliminates discrepancies between different departments and provides a single source of truth. Retailers can easily access and analyze inventory data, helping them make informed decisions about stock levels, promotions, and supplier relationships.
2. Improved Sales and Order Fulfillment
ERP systems also play a pivotal role in enhancing sales and order fulfillment processes:
Integrated Sales Channels: ERP software integrates with various sales channels, including physical stores, e-commerce platforms, and mobile apps. This integration ensures that sales data is synchronized across all channels, providing a unified view of sales performance and customer behavior.
Enhanced Customer Experience: By integrating with Customer Relationship Management (CRM) modules, ERP systems offer insights into customer preferences and purchase history. This information enables personalized marketing and sales strategies, leading to improved customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Efficient Order Processing: ERP systems streamline order processing by automating key tasks such as order entry, invoicing, and shipping. This reduces the time required to fulfill orders and minimizes errors. Retailers can process a higher volume of orders quickly and accurately, which enhances customer experience and boosts sales.
3. Data-Driven Insights
ERP software provides powerful analytics and reporting tools that help retailers make data-driven decisions:
Sales Analytics: ERP systems generate detailed reports on sales performance, including trends, top-selling products, and sales by location. Retailers can analyze this data to identify sales patterns, optimize product assortments, and plan targeted promotions.
Inventory Analytics: By analyzing inventory turnover rates, stock levels, and supplier performance, retailers can make informed decisions about inventory management. ERP systems help identify slow-moving items, optimize stock levels, and negotiate better terms with suppliers.
Forecasting and Planning: ERP systems use historical data to forecast future demand and plan inventory levels accordingly. This helps retailers anticipate market trends, plan for seasonal variations, and make strategic decisions about stock procurement.
4. Integration with Supply Chain
ERP systems facilitate better coordination with suppliers and other partners in the supply chain:
Supplier Management: ERP software provides tools for managing supplier relationships, tracking purchase orders, and evaluating supplier performance. This improves communication and ensures timely deliveries.
Supply Chain Visibility: With ERP, retailers gain visibility into the entire supply chain, from procurement to delivery. This helps in managing lead times, identifying bottlenecks, and optimizing supply chain operations.
Cost Management: By integrating procurement and inventory management, ERP systems help retailers control costs and negotiate better pricing with suppliers. This can lead to significant cost savings and improved profitability.
5. Scalability and Flexibility
As retail businesses grow, ERP systems offer scalability and flexibility to adapt to changing needs:
Multi-Store Management: For retailers with multiple locations, ERP systems provide centralized management of all stores. This simplifies inventory control, sales tracking, and reporting across different locations.
E-Commerce Integration: ERP systems seamlessly integrate with e-commerce platforms, allowing retailers to manage online sales alongside in-store operations. This ensures a cohesive omnichannel experience for customers.
Customizable Modules: ERP software offers customizable modules that can be tailored to specific retail needs. Whether it’s advanced inventory management features or specialized sales reporting, retailers can configure the system to meet their unique requirements.
Conclusion
ERP software is a powerful tool for enhancing inventory management and driving sales in the retail sector. By providing real-time inventory tracking, automating reordering, integrating sales channels, and offering data-driven insights, ERP systems enable retailers to optimize their operations, improve customer satisfaction, and achieve business growth. As the retail landscape continues to evolve, investing in a robust ERP solution can provide a competitive edge and support long-term success.